Module Dependency Analysis
Introduction
Rsdoctor provides the Module Imported Chain Analysis module, which is mainly used to analyze the dependency tree of a specific module, i.e. the modules that depend on it, similar to Webpack's stats.reasons.
In this section, you can analyze the imported chain of a module. If you have the need to split the package or want to see why a certain module is being imported, you can quickly and clearly locate the reference chain through the Module Imported Chain Analysis.
This Section’s Entry
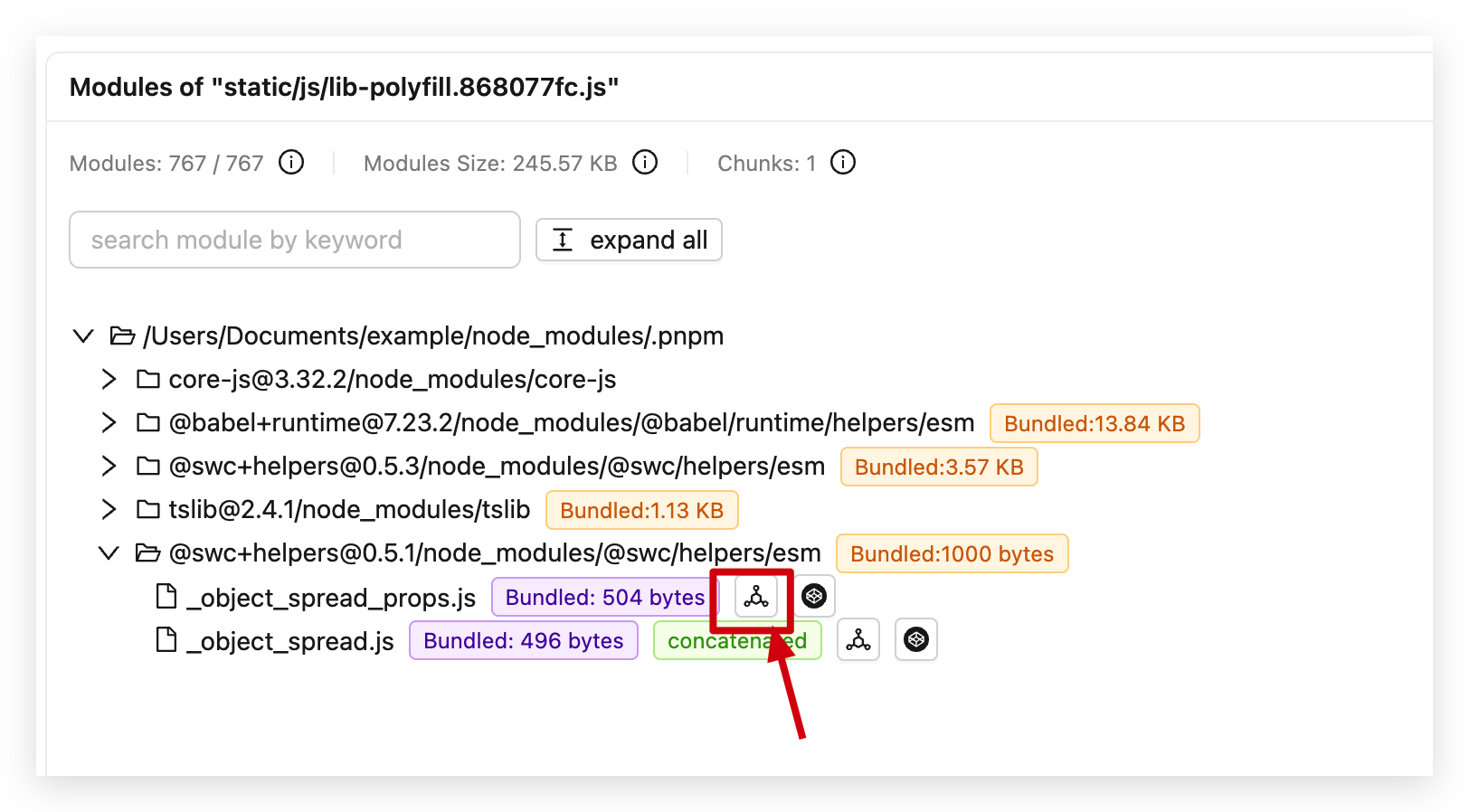
Clicking on an Assets in the Bundle Size page will display the 「Module Tree」 on the right side. Each Module will have the following icon next to it, click on it to view the imported chain of that Module.
Glossary
Reasons: As the name suggests, it means the reasons why aModuleexists. Reasons indicate which otherModules import thisModule, and the entireReasons Treerepresents the upstream reference chain of thisModule, including both direct and indirect parentModules. Similar to Webpack's stats.reasons.Dependencies: TheModules that thisModuledepends on.
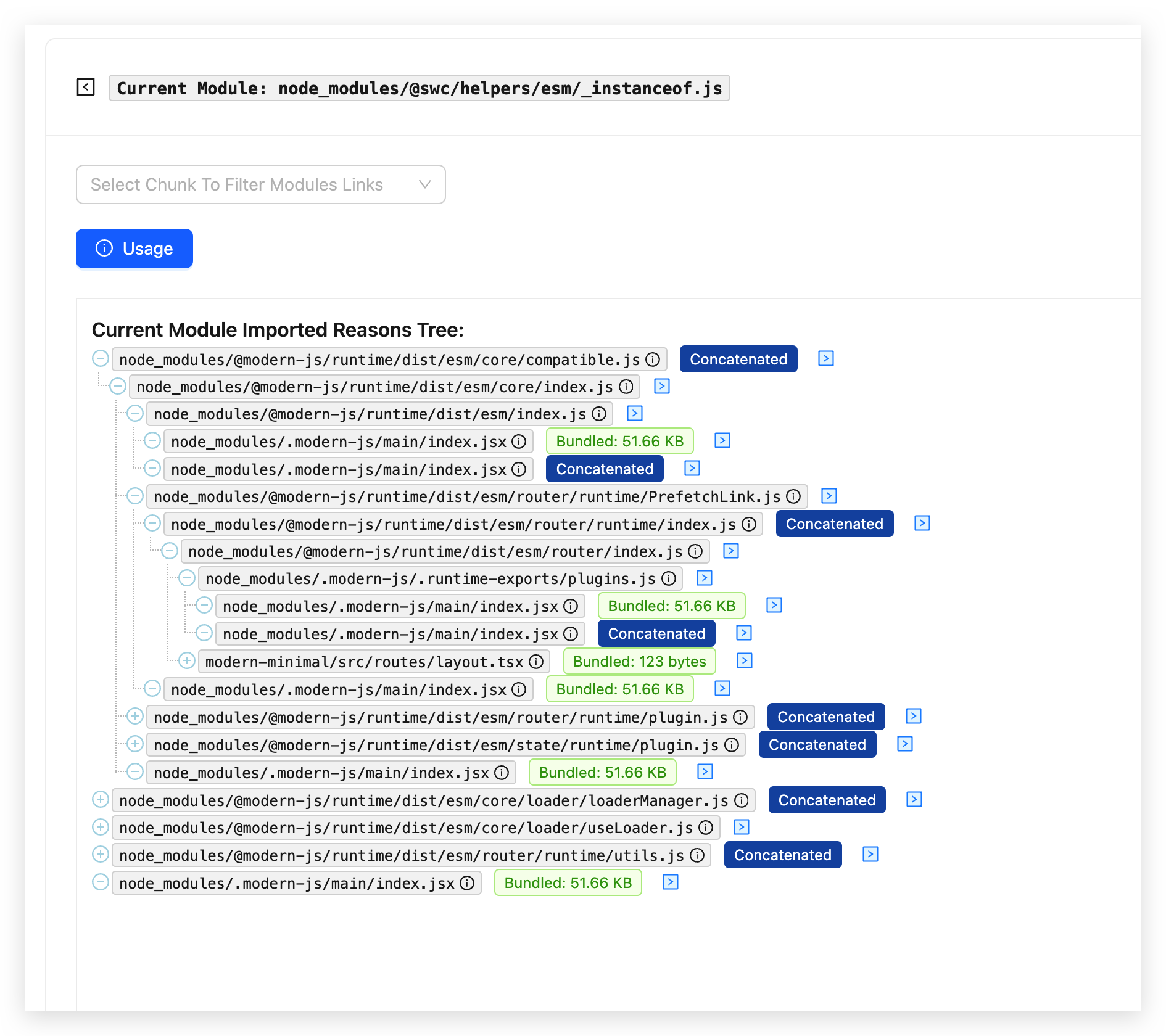
Reasons Dependency Tree
Introduction
The Reasons Tree displays the dependency chain of this Module, showing which other Modules directly or indirectly import it. In this dependency tree, you can view the Bundled Size of the Modules along the dependency chain. You can also click the right arrow > to navigate to the Module Dependency Analysis page for that specific Module.
- Parent-child relationship in the dependency tree: The parent node file is the one that is depended upon by the child node file and is therefore bundled into the output. Similarly, the grandchild node file is depended upon by the child node and is bundled into the output, and so on.
-
The
Usagetag displays the purpose of various module tags. -
The
Concatenatedtag:- The
Concatenatedtag indicates that the module is a concatenated sub-module. Hover over it to see which main module it is aggregated into. This type of aggregated module cannot be further unpacked, so the specificBundled Sizecannot be determined, only the size of the entire concatenated module can be known. - Glossary: A concatenated module is when multiple modules are promoted or concatenated into a closure during packaging. For an explanation of
Concatenated Module, refer to the Glossary.
- The
-
The
!tag, hover over it to display the detailed path of the module.
